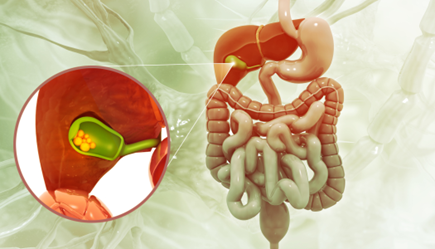
A tiny organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, a fluid essential for digesting fats. Solid particles form in the gallbladder, and these stones obstruct the normal flow of bile, leading to a range of health issues.
Risk Factor
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing gallstones:
- Gender and Age: Women over the age of 40 are more prone to developing gallstones due to hormonal changes, particularly related to estrogen.
- Weight Issues: Being overweight or obese can elevate cholesterol levels in bile, contributing to the formation of gallstones.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can cause an imbalance in bile composition, promoting the growth of gallstones.
- Diet Choices: Diets that are high in cholesterol, saturated fats, and sugars can encourage the development of gallstones.
- Family History: If gallstones run in your family, your risk of developing them is higher.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes and liver disease can increase the risk of gallstones by altering the balance of substances in bile.
Symptoms triggers
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Jaundice
Preventing Gallstones
While some risk factors for gallstones are beyond your control, there are several proactive steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing the intake of processed foods can also help prevent gallstones.
- Gradual Weight Loss: If weight loss is needed, aim for a gradual reduction through a healthy diet and regular exercise to avoid disrupting bile composition.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water helps support digestion and prevents the formation of gallstones by keeping bile fluid.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity for managing weight and lowering the risk of gallstones.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Incorporating fibre-rich foods into your diet supports digestive health and helps maintain proper bile composition.
Gallstones are diagnosed using the following methods:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique is the most common method for detecting gallstones and assessing their size.
- CT scan: A more detailed imaging method that can identify gallstone complications.
- Blood Tests: Tests can detect signs of infection, inflammation, or other complications caused by gallstones.
Gallstones, though common, can significantly impact digestive health if not properly managed. People can actively maintain gallbladder health and overall well-being by understanding the causes, risks, and preventative measures. If you suspect you have gallstones or are at risk, seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and personalized guidance.